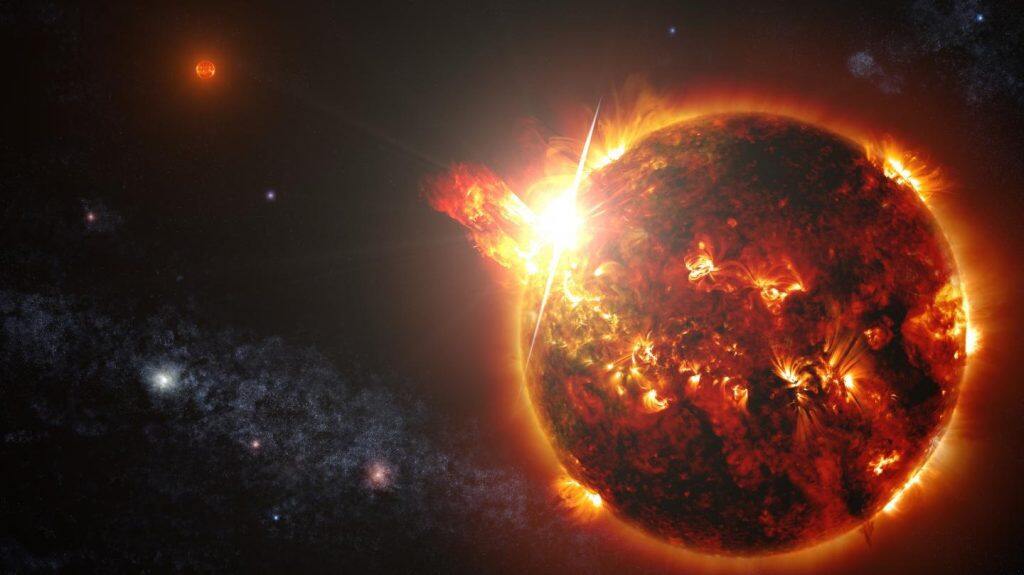

Although violent and unpredictable, stellar flares emitted by a planet’s host star do not necessarily prevent life from forming, according to a new Northwestern University study.
Emitted by stars, stellar flares are sudden flashes of magnetic energy. On Earth, the sun’s flares sometimes damage satellites and disrupt radio communications. Elsewhere in the universe, however, robust stellar flares also have the ability to deplete and destroy atmospheric gases, such as ozone. The destruction of gases like ozone could allow harmful levels of ultraviolet (UV) radiation to penetrate a planet’s atmosphere, thereby diminishing its chances of harboring surface life.
By combining 3D atmospheric chemistry and climate modeling with observed flare data from distant stars, a Northwestern-led team discovered that stellar flares could play an important role in the long-term evolution of a planet’s atmosphere and habitability.
“We compared the atmospheric chemistry of planets experiencing frequent flares with planets experiencing no flares. The long-term atmospheric chemistry is very different,” said Northwestern’s Howard Chen, the study’s first author. “Continuous flares actually drive a planet’s atmospheric composition into a new chemical equilibrium.”
“We’ve found that stellar flares might not preclude the existence of life,” added Daniel Horton, the study’s senior author. “In some cases, flaring doesn’t erode all of the atmospheric ozone. Surface life might still have a fighting chance.”
The study was published today (Dec. 21) in the journal Nature Astronomy. It is a joint effort among researchers at Northwestern, University of Colorado at Boulder, University of Chicago, Massachusetts Institute of Technology and NASA Nexus for Exoplanet System Science (NExSS).
Horton is an assistant professor of Earth and planetary sciences in Northwestern’s Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences. Chen is a Ph.D. candidate in Horton’s Climate Change Research Group and a NASA future investigator. They are both members of Northwestern’s Center for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Research in Astrophysics (CIERA).
All stars — including our very own sun — flare, or randomly release stored energy. Fortunately for Earthlings, the sun’s flares typically have a minimal impact on the planet.
“Our sun is more of a gentle giant,” said Allison Youngblood, an astronomer at the University of Colorado at Boulder and co-author of the study. “It’s older and not as active as younger and smaller stars. Earth also has a strong magnetic field, which deflects the sun’s damaging winds.”
Unfortunately, most potentially habitable exoplanets aren’t as lucky. For planets to potentially harbor life, they must be close enough to a star that their water won’t freeze — but not so close that water vaporizes.
“We studied planets orbiting within the habitable zones of M and K dwarf stars — the most common stars in the universe,” Horton said. “Habitable zones around these stars are narrower because the stars are smaller and less powerful than stars like our sun. On the flip side, M and K dwarf stars are thought to have more frequent flaring activity than our sun, and their tidally locked planets are unlikely to have magnetic fields helping deflect their stellar winds.”
Chen and Horton previously conducted a study of M dwarf stellar systems’ long-term climate averages. Flares, however, occur on an hours- or days-long timescales. Although these brief timescales can be difficult to simulate, incorporating the effects of flares is important to forming a more complete picture of exoplanet atmospheres. This is accomplished by incorporating stellar flare data from NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Satellite Survey, launched in 2018, into their model simulations.
If there is life on these M and K dwarf exoplanets, previous work hypothesizes that stellar flares might make it easier to detect. For example, stellar flares can increase the abundance of life-indicating gasses (such as nitrogen dioxide, nitrous oxide and nitric acid) from imperceptible to detectable levels.
“Space weather events are typically viewed as a detriment to habitability,” Chen said. “But our study quantitatively showed that some space weather can actually help us detect signatures of important gases that might signify biological processes.”
This study involves researchers from a wide range of backgrounds and expertise, including climate scientists, exoplanet scientists, astronomers, theorists and observers.
“This project was a result of fantastic collective team effort,” said Eric T. Wolf, a planetary scientist at CU Boulder and a co-author of the study. “Our work highlights the benefits of interdisciplinary efforts when investigating conditions on extrasolar planets.”
The study, “Persistence of flare-driven atmospheric chemistry on rocky habitable zone worlds,” was supported by the NASA Earth and Space Science and Technology Graduate Research Award (number 80NSSC19K1523).







































