Berberine, a natural compound found in plants such as barberry and goldenseal, shows promise for the treatment of lung diseases.


Berberine, a natural compound found in plants such as barberry and goldenseal, supresses the proliferation of lung cancer cells in the lab, new research shows. It also reduces airway inflammation and damage to healthy lung cells exposed to chemicals from cigarette smoke.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer related deaths globally, with around 1.8 million deaths reported annually. Chronic inflammation is a risk factor for lung cancer and other diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
“Berberine has shown therapeutic benefits for diabetes and cardiovascular disease. We were keen to explore its potential in supressing lung cancer and reducing inflammation,” says lead researcher Dr Kamal Dua, a senior lecturer in Pharmacy and Senior Research Fellow, Australian Research Centre in Complementary and Integrative Medicine (ARCCIM), Faculty of Health at the University of Technology Sydney (UTS).
The evaluation of berberine’s effect on non-small cell lung cancer has just been published in the journal Pharmaceutics. It shows that berberine exhibits potent anticancer activity, supressing cancer cell growth in vitro.


The potential mechanism of action for anti-cancer activity was determined by measuring the mRNA levels of tumour-associated genes and protein expression levels. It showed that berberine upregulates tumour suppressor genes, and downregulates proteins involved in cancer cell migration and proliferation.
The study follows research recently published in Antioxidants, also led by Dr Dua, showing berberine can inhibit oxidative stress, and reduce inflammation and cellular senescence induced by cigarette smoke extract in lab-grown human healthy lung cells.
The research team includes Professor Phil Hansbro, Professor Brian Oliver, Dr Bikash Manandhar and Dr Keshav Raj Paudel along with international collaborators from the International Medical University in Malaysia and Qassim University in Saudi Arabia.
Dr Dua’s focus is on exploring the curative potential of traditional medicinal plants and how their active compounds work at the cellular level. He has a multi-faceted research background with experience in drug delivery technology, biomedical sciences, immunology and microbiology.
Berberine has long been used in traditional Chinese and Ayruvedic medicine, however its therapeutic benefits have been limited by its lack of water solubility and absorption in the gut, as well as toxicity at higher doses.
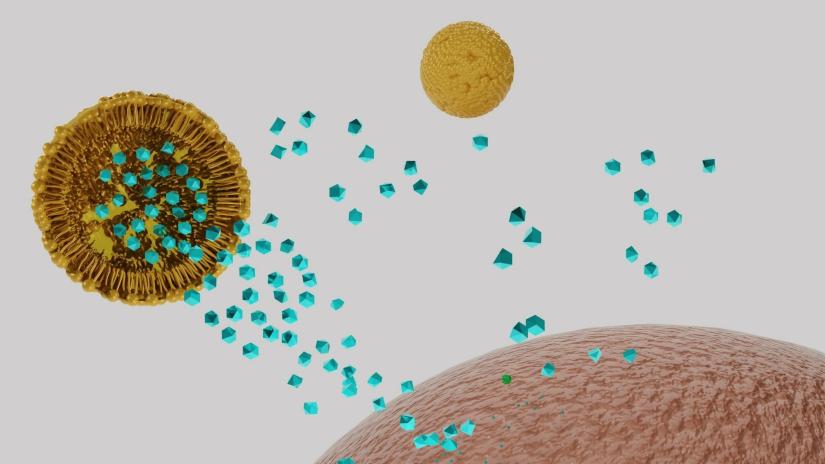

To overcome these challenges Dr Dua has developed the use of liquid crystalline nanoparticles, an advanced drug delivery system that encapsulates berberine in tiny soluble and biodegradable polymer balls to enhance safety and effectiveness.
Decades of research has shown that cigarette smoke is toxic to lung cells, causing inflammation of the airways and hastening diseases such as cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
The researchers found that berberine supressed the generation of inflammatory chemicals, called reactive oxygen species, which cause damaging effects to cells. It also modulated genes involved in inflammation, oxidative stress, and reduced premature cell senescence.
Dr Dua is now in discussion and working closely with Sydney based companies to take this research to the next level and identify the best formulation and delivery system for these nanoparticles, so that it can be translated to the bedside.