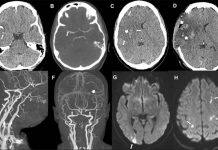
Covid-19 vaccine: Common stroke symptoms must be ‘urgently evaluated’
UCL and UCLH neurologists have published the first clinical observations of patients who experienced an ischaemic stroke, the most common form of stroke, following an Oxford AstraZeneca vaccine.
Innovation, leadership and purpose in a post-pandemic world
Everyone is currently trying to picture what the future will look like after the COVID-19 pandemic has passed, how markets will be shaped...
Student depression, anxiety soaring during pandemic, new survey finds
The COVID-19 pandemic appears to be driving dramatic increases in depression and anxiety among college students, with more than a third reporting significant mental health challenges
Tracking the economic impacts of COVID-19 one ship at a time
COVID-19 saw global maritime trade collapse by as much as 10% in the first eight months of 2020 – leading to losses of up to $412 billion, reveals recently published Oxford research...
The power of peer-to-peer communication in the COVID-19 vaccine rollout: study
During the COVID-19 pandemic, discussions with peers played a large role in people’s decisions around vaccination, new research from UNSW Sydney shows.
UK National Health Service begins rollout of Oxford coronavirus vaccine
The Oxford AstraZeneca vaccinations will be delivered at a small number of hospitals for the first few days for surveillance purposes, as is standard practice, before the bulk of supplies are...
Study: Therapy Leads to Fewer Hospital Readmissions for Pneumonia Patients
Pneumonia—inflammation in the lungs—has long been a leading cause of hospitalization and death in the United States, even before the pandemic.
Study reveals mouth as primary source of COVID-19 infection
A team of researchers led by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research reveals coronavirus...
Policies for COVID-19 elimination, not mitigation, best for health, economy and civil liberties
Countries which aimed to eliminate COVID-19 registered fewer deaths, better economic performance and fewer restrictions and lockdowns, according to an article in The Lancet.
High blood pressure and its drug treatment unlikely to increase entry of COVID-19 virus...
Fears that people with high blood pressure are more at risk from severe Covid-19 because it is easier for the virus to enter their cells and tissues have been laid to rest...